Innovative Catalysts for Durable Fuel Cells in Hard-to-Decarbonize Sectors
Key Ideas
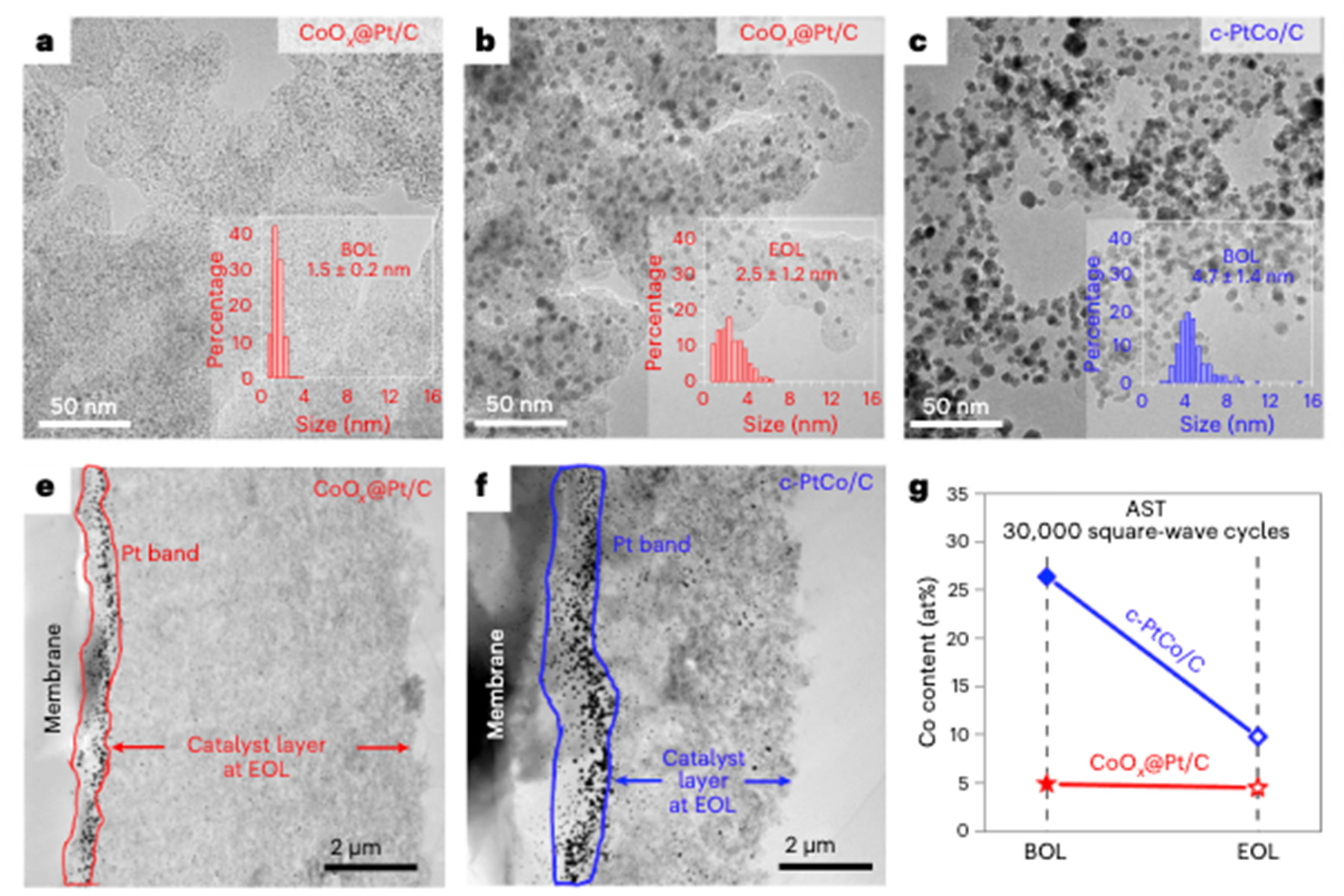
- Embedding cobalt oxide clusters in platinum catalysts increases longevity of PEM fuel cells by 87.5%, surpassing industry standards.
- Fuel cells are considered optimal for hard-to-decarbonize sectors like heavy-duty transport due to higher energy density and platinum scarcity.
- Research at UCLA Samueli School of Engineering showcases a novel atomic scaffold that enhances stability of platinum atoms within catalysts.
- While facing platinum scarcity, global efforts focus on advancing PEM fuel cell technology through innovative catalyst designs like cobalt-oxide clusters.
A recent study published in Nature Catalysis by UCLA Samueli School of Engineering introduces a groundbreaking method to enhance the longevity of proton-exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells. Led by Professor Yu Huang, the research team embedded cobalt oxide clusters in ultrafine platinum catalysts, outperforming traditional platinum-cobalt alloys in durability. The study's findings indicate that fuel cells equipped with these catalysts could last significantly longer than current industry standards, particularly benefiting heavy-duty transport applications. The research highlights the crucial role of fuel cells in hard-to-decarbonize sectors, such as long-haul transport and maritime applications, where their energy density and platinum scarcity make them a preferred choice. Despite the platinum reliance of hydrogen PEM technology, ongoing international efforts seek to replace platinum with more abundant materials like iron. The study, funded in part by the U.S. Office of Naval Research, underscores the importance of advancing fuel cell technology for sustainable energy solutions, aligning with global initiatives for decarbonization and energy independence.