Unlocking the Potential: Single-Atom Alloys Revolutionizing Bio-Oil to Hydrogen Conversion
Key Ideas
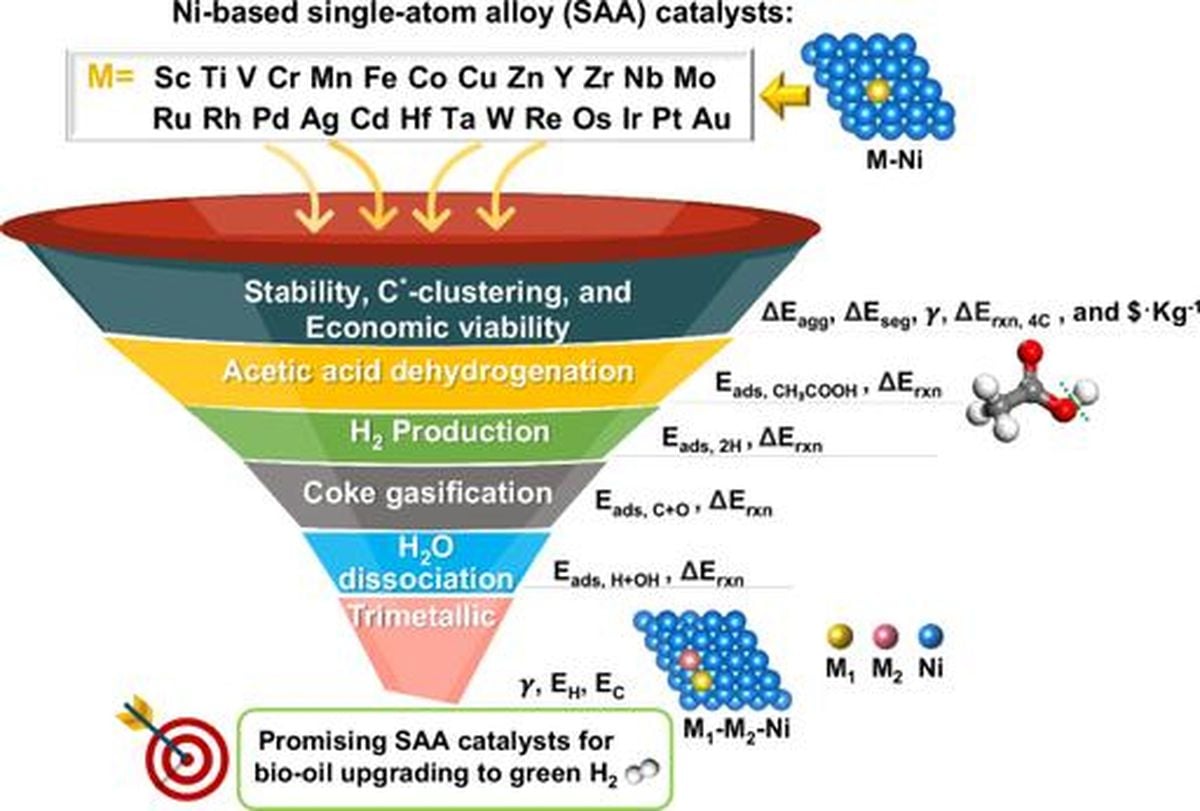
- Researchers are investigating nickel-based single-atom alloys (SAAs) to convert acetic acid in bio-oils into hydrogen, a key step in creating a sustainable hydrogen economy.
- The study utilized density functional theory to assess stability and activity of various SAAs, identifying Pd-Ni and Cu-Ni alloys as promising for hydrogen production and desorption.
- Six novel trimetallic combinations were discovered to be stable and resistant to catalyst deactivation, offering potential for efficient hydrogen production from renewable biofuels.
- Theoretical advancements in catalyst design could lead to more affordable and high-performance systems, aligning with global sustainability objectives and addressing climate change challenges.
In a breakthrough study, researchers are exploring the potential of single-atom alloys (SAAs) in efficiently converting bio-oil into hydrogen fuel, a crucial step towards establishing a sustainable hydrogen economy. The focus of the research lies in the utilization of nickel-based SAAs to catalyze the conversion of acetic acid, a significant component in bio-oils, into hydrogen. The study addresses the challenge of developing cost-effective and stable catalysts for bio-oil steam reforming, a key process in hydrogen production from renewable sources. While SAAs have shown promise due to their high activity and cost-effectiveness, concerns regarding their long-term stability in reaction environments have been raised. To evaluate the performance of various nickel-based SAAs, researchers employed density functional theory (DFT) calculations to analyze stability, activity, and regeneration capabilities. The results highlighted the exceptional hydrogen production rates of the Pd-Ni alloy and the superior hydrogen desorption capacity of the Cu-Ni alloy. Additionally, the study identified six new trimetallic combinations with high stability and resistance to catalyst deactivation, offering potential for enhanced hydrogen production from biofuels. The research signifies a significant step towards the application of advanced materials in energy conversion processes, emphasizing the importance of affordable and efficient catalysts in driving the transition towards cleaner energy solutions. By combining affordability with improved catalytic performance, the findings have the potential to advance the development of cleaner hydrogen production systems, contributing to global sustainability goals and addressing climate change and energy resource challenges.