Enhancing Electrochemical Technologies: Ruthenium-Doped Mn-Oxides for Sustainable Hydrogen Production
Key Ideas
- Platinum-free electrocatalysts are crucial for anion exchange membrane fuel cells and water electrolysers.
- Ruthenium doping of Li-intercalated layered Mn-oxides enhances catalyst performance for hydrogen technologies.
- The study aims to improve the techno-economic viability of electrochemical technologies for sustainable hydrogen production.
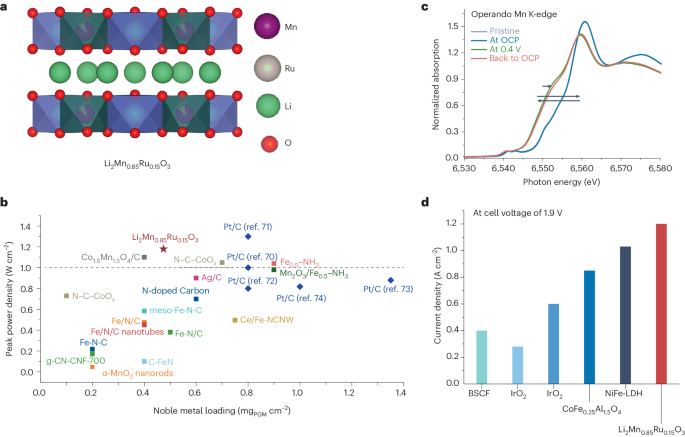
- Li2Mn0.85Ru0.15O3 shows promising results as an efficient oxygen catalyst for AEMFCs and AEMWEs.
The article discusses the need for platinum-free electrocatalysts to advance anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs) and water electrolyzers (AEMWEs) for the sustainable production of hydrogen. Researchers have focused on modifying the electronic structure of Li-intercalated layered Mn-oxides through Ruthenium (Ru) doping. This modification has led to a significant improvement in catalyst performance for both technologies. The study's main objective is to enhance the techno-economic viability of these electrochemical technologies to promote the sustainable production and utilization of hydrogen. The catalyst, Li2Mn0.85Ru0.15O3, has demonstrated impressive results as an efficient oxygen catalyst for AEMFCs and AEMWEs, showcasing its potential in advancing hydrogen-related technologies. Overall, the research highlights the importance of innovative catalyst development to drive the adoption of hydrogen as a clean energy source.