Innovative Design of Pt Cluster-W3O/WC Catalyst for Enhanced Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction Efficiency
Key Ideas
- Development of a novel Pt cluster-W3O/WC catalyst for efficient hydrogen oxidation reaction in PEMFCs.
- The catalyst exhibits superior mass activity and anti-CO poisoning capability compared to commercial Pt/C.
- The collaboration between tungsten oxide and carbide enhances HOR activity and reduces the reliance on platinum, promising advancements in fuel cell technology.
- The study provides insights into the reaction mechanisms involving the composite materials, highlighting the importance of experimental data for electrocatalytic processes.
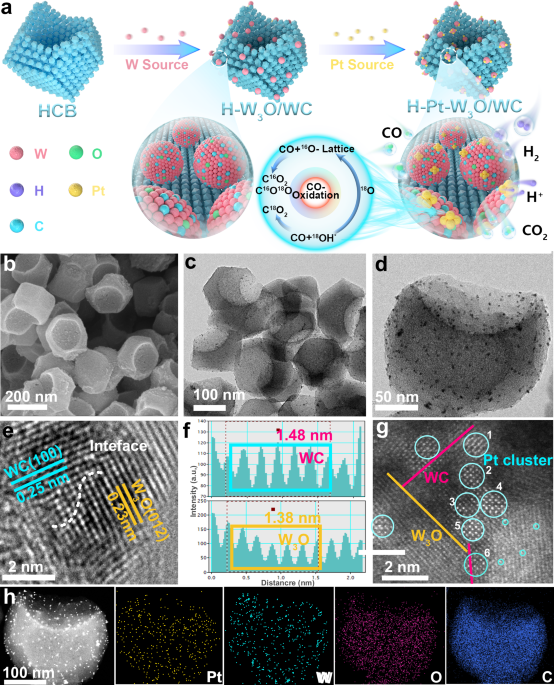
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are crucial for the hydrogen energy sector's growth. This study introduces a new electrocatalyst, H-Pt-W3O/WC, designed to improve hydrogen oxidation efficiency and reduce CO poisoning in PEMFCs. By combining a hollow carbon skeleton-supported Pt cluster-W3O/WC heterojunction, the catalyst achieves significantly higher mass activity and anti-CO poisoning capability than traditional Pt/C. The collaborative effect of tungsten oxide and carbide enhances the catalyst's performance, potentially decreasing the dependence on platinum. Structural characterization reveals the efficient synthesis of the catalyst, with Pt existing as clusters on the surface. The study delves into the mechanisms of the catalytic reactions, emphasizing the need for comprehensive experimental data in electrocatalysis research. Overall, the innovative design of the Pt cluster-W3O/WC catalyst shows promise for advancing fuel cell technology towards sustainable energy systems.
Topics
Fuel Cells
Sustainability
Research
Energy Systems
Catalysts
Electrocatalysis
Materials Science
Reactive Metals
Latest News