Innovative Electrochemical Approach for Urea Treatment and Hydrogen Production
Key Ideas
- Urea overuse in agriculture poses environmental and health risks, motivating the development of sustainable treatment methods.
- The electrochemical urea oxidation reaction offers a promising solution for denitrification and hydrogen production.
- The study explores the use of atomically isolated Ni-O-Ti sites for enhanced urea conversion to N2 and efficient hydrogen evolution.
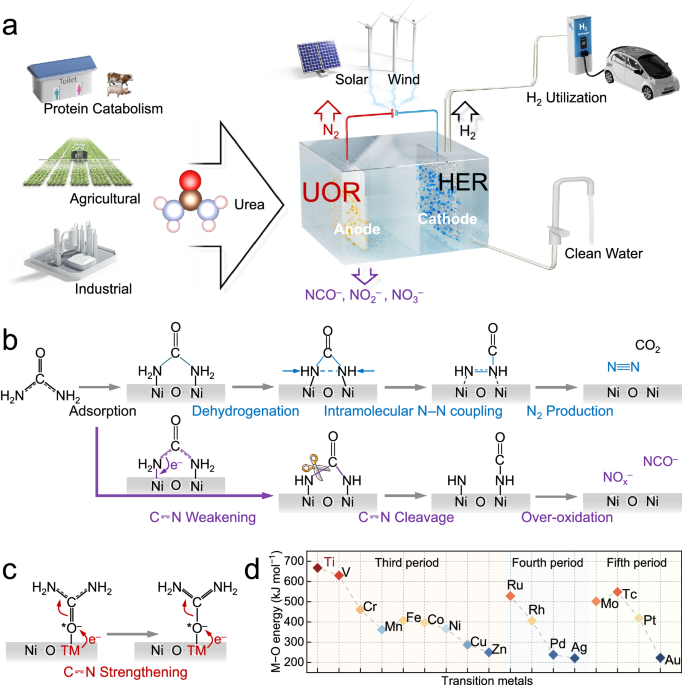
Urea, a crucial biomolecule, is excessively used in agriculture, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. Traditional treatment methods are complex and energy-intensive. However, urea's potential as a hydrogen carrier has spurred research into innovative solutions for urea-containing wastewater treatment and hydrogen production. The electrochemical urea oxidation reaction (UOR) shows promise for denitrification and hydrogen generation, particularly when coupled with the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). The study focuses on developing efficient UOR catalysts to enhance urea conversion to N2, avoiding harmful byproducts. By creating atomically isolated Ni-O-Ti sites, the research aims to strengthen urea's C⎓N bonds and improve N2 selectivity, crucial for sustainable urea treatment and hydrogen production. The proposed prototype device combines an electrode with Ni-O-Ti sites for UOR and a Pt cathode for H2 evolution, powered by solar energy. This innovative approach showcases the potential for decentralized fuel production and efficient urea waste management.