Revolutionizing Clean Energy: The Power of High-Entropy Alloy Catalysts
Key Ideas
- A novel high-entropy alloy (HEA) catalyst, PtPdCoNiMn, has been developed in Bengaluru to enhance hydrogen production through water electrolysis, offering a more efficient and cost-effective alternative to traditional catalysts.
- The PtPdCoNiMn HEA catalyst reduces reliance on expensive materials like platinum, using seven times less platinum while maintaining better catalytic efficiency and sustainability in hydrogen generation methods.
- The innovative synthesis methods of the catalyst, involving electrodeposition and solvothermal processes, have yielded impressive results in terms of hydrogen production efficiency, durability, and stability, even in challenging environments like alkaline seawater.
- Funded by India's Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) and overseen by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), this breakthrough research not only revolutionizes hydrogen production but also holds promise for cleaner and more affordable energy solutions across various industries and renewable technologies.
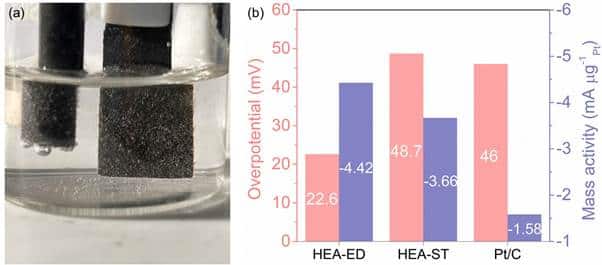
The development of a new alloy-based catalyst in Bengaluru has sparked excitement in the field of clean energy production. This innovative catalyst, known as a high-entropy alloy (HEA) named PtPdCoNiMn, has shown remarkable potential in enhancing hydrogen production through water electrolysis. By leveraging the unique properties of HEAs, this catalyst offers a more efficient and cost-effective alternative to traditional catalysts, reducing the reliance on expensive materials like platinum. Researchers at the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS) overcame challenges in preparing single-phase nanoparticles by designing the PtPdCoNiMn catalyst based on guidelines from Dr. Prashant Singh of the AMES National Laboratory in the USA. The synthesis methods involved electrodeposition at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, as well as chemical synthesis through solvothermal processes at high temperature and pressure. These methods led to the successful production of a catalyst that demonstrated impressive efficiency in hydrogen production, with minimal energy loss and high durability. The PtPdCoNiMn HEA catalyst's optimal binding of reaction intermediates on the catalyst surface contributed to its superior performance compared to commercial catalysts. The catalyst's reduced reliance on platinum, using significantly less while maintaining better efficiency, not only lowers production costs but also enhances the sustainability of hydrogen production methods. It has proven its stability and efficiency for over 100 hours even in challenging environments like alkaline seawater. This breakthrough, funded by India's Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) and overseen by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), not only revolutionizes hydrogen production but also has broader implications for cleaner and more affordable energy solutions in various industries and renewable technologies.
Topics
Production
Renewable Energy
Clean Energy
Sustainability
Research
Catalysts
Nanoparticles
Efficiency
Cost-effective
Latest News