Tuning Catalysts for Clean Hydrogen and Crucial Co-Products
Key Ideas
- Researchers at Stanford University have developed a catalyst that can co-produce acetic acid alongside clean hydrogen with high selectivity and minimal CO2 emissions.
- The article highlights the importance of finding market space for co-products associated with producing hydrogen through zero-carbon processes.
- The research aims to help access new markets by diversifying the range of valuable chemicals that can be produced alongside hydrogen.
- This innovative approach contributes to sustainable fuel production and reduces environmental impact by minimizing CO2 emissions.
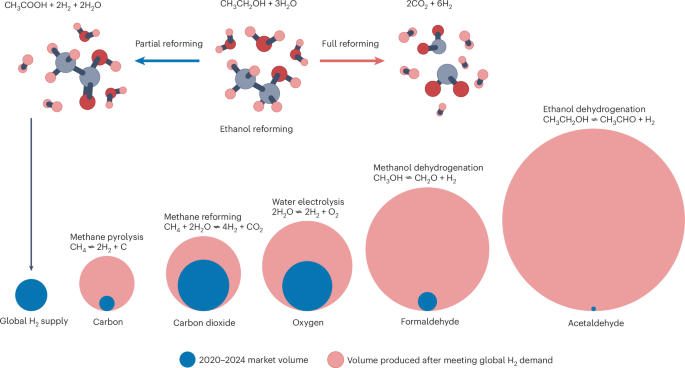
The article discusses a significant development in the production of clean hydrogen and associated co-products. Researchers at Stanford University have fine-tuned a catalyst to not only generate clean hydrogen but also produce acetic acid—an essential commodity chemical. This breakthrough enables the co-production of valuable chemicals alongside hydrogen using zero-carbon processes, contributing to sustainability efforts.
The study emphasizes the challenge of finding market space for co-products generated during hydrogen production. By diversifying the range of chemicals that can be produced alongside hydrogen, researchers aim to open up new markets and create added value. This approach helps meet the global demand for hydrogen while also addressing the need for sustainable and environmentally friendly fuel sources.
The catalyst developed by the researchers demonstrates high selectivity and minimal CO2 emissions, highlighting its efficiency in clean fuel production. By focusing on producing not just hydrogen but also valuable chemicals like acetic acid, the research facilitates a more holistic and environmentally conscious approach to fuel production.
Overall, the article showcases the positive impact of innovative catalyst tuning on sustainable fuel production. Through the co-production of valuable chemicals alongside hydrogen, this research contributes to advancing clean energy technologies and reducing the environmental footprint of fuel production processes.