Innovative Electrolysis Catalyst: Halogen-Doped Graphene for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution
Key Ideas
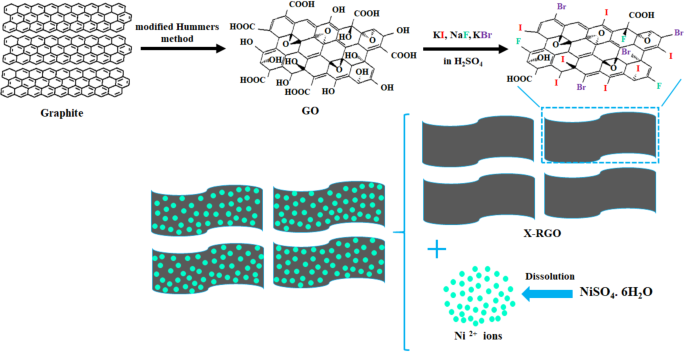
- Development of halogen-doped reduced graphene oxide with nickel nanoparticles shows promising results for hydrogen evolution reactions.
- The study focuses on improving electrocatalytic performance using cost-effective and efficient non-noble metals like nickel.
- Heteroatom doping on graphene surfaces enhances catalytic behavior by providing additional active sites and increasing the electrochemical active area.
- Halogen-doped graphene offers a novel approach to developing highly efficient and cost-effective non-precious metal electrocatalysts for hydrogen production.
The scientific article explores the development of a novel electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) by using halogen-doped reduced graphene oxide with nickel nanoparticles. The study aims to enhance the catalytic behavior of catalysts to improve hydrogen production efficiency. By doping heteroatoms on graphene surfaces, the researchers achieved a significant improvement in the electrochemical performance of the catalyst, leading to a promising cathodic electrode for HER. The presence of halogens in the reduced graphene oxide influenced the charge distribution on the graphene surface, exposing additional active sites and extending the electrochemical active area. This approach offers a cost-effective alternative to noble metal catalysts and demonstrates high efficiency in hydrogen evolution. The study emphasizes the importance of transitioning to non-precious metal electrocatalysts for sustainable hydrogen production. Carbon-based materials play a crucial role as effective carriers for HER catalysts due to their stability and high electrical conductivity. The integration of nickel nanoparticles into halogen-doped graphene showcases a new pathway for developing efficient and affordable catalysts. Overall, the research contributes to the ongoing efforts to find renewable and sustainable energy solutions, highlighting the significance of innovative electrocatalysts in advancing the field of hydrogen production.